Coding
Code analysis, GitHub integration, and development tools to enhance your coding workflow
Table of Contents
Overview
The Coding plugins and agents are designed to help developers write, evaluate, and analyze code more efficiently. These plugins provide a range of functionalities, from commenting and evaluating code snippets to extracting code from GitHub pages and analyzing Git repositories. By leveraging these plugins, developers can enhance their coding practices, improve code quality, and ensure the security of their codebase.
List of Coding Plugins & Agents
This plugin lets you comment your source code
This plugin lets you evaluate source code
Get the source code from a GitHub page
Scan a Git repository for security vulnerabilities, performance issues, and other problems
Search a GitHub repo for specific text
Comment
The Comment plugin is designed to enhance code readability and maintainability. It allows developers to easily add comments to their codebase, making it more understandable. It is particularly useful for those who have inherited a codebase and want to gain a better understanding of the code or for those who want to improve the documentation of their code.
import pandas as pd
def filter_and_sum_function(file_path, column_filters, delimiter=None, sum_columns=None):
if file_path.endswith('.xlsx'):
user_file = pd.read_excel(file_path)
elif file_path.endswith('.txt') and delimiter:
user_file = pd.read_csv(file_path, delimiter=delimiter)
else:
raise ValueError("Unsupported file type or missing delimiter for text files.")
print("DataFrame before filtering:")
display(user_file.head())
start_count = len(user_file)
for column, filters in column_filters.items():
if column not in user_file.columns:
print(f"Warning: Column '{column}' does not exist in the DataFrame.")
continue
filter_condition = pd.Series([False] * len(user_file))
for filter_value in filters:
if pd.api.types.is_string_dtype(user_file[column]):
filter_condition |= user_file[column].str.contains(filter_value, case=False, na=False)
elif pd.api.types.is_numeric_dtype(user_file[column]):
try:
filter_value_numeric = float(filter_value)
filter_condition |= (user_file[column] == filter_value_numeric)
except ValueError:
print(f"Warning: '{filter_value}' is not a valid number for column '{column}'.")
else:
print(f"Warning: Column '{column}' has unsupported data type for filtering.")
user_file = user_file[filter_condition]
print("Filtered DataFrame:")
display(user_file)
count = len(user_file)
total_sums = {col: user_file[col].sum() for col in sum_columns} if sum_columns else None
print(f"Total number of rows in the file before filtering: {start_count}")
print(f'Count of filtered entries: {count}')
if sum_columns:
for col, total in total_sums.items():
print(f'Total sum of {col} in filtered entries: {total}')import pandas as pd
def filter_and_sum_function(file_path, column_filters, delimiter=None, sum_columns=None):
"""
This function reads a file, filters the data based on user-defined column filters,
and calculates the sum of specified columns in the filtered data.
Parameters:
- file_path (str): Path to the file to be processed.
- column_filters (dict): Dictionary containing column names as keys and a list of filter values as values.
- delimiter (str, optional): Delimiter used in case of a text file. Default is None.
- sum_columns (list, optional): List of column names to calculate the sum. Default is None.
Raises:
- ValueError: If the file type is not supported or if a delimiter is missing for text files.
Returns:
- None
"""
# Read the file based on the file type
if file_path.endswith('.xlsx'):
user_file = pd.read_excel(file_path)
elif file_path.endswith('.txt') and delimiter:
user_file = pd.read_csv(file_path, delimiter=delimiter)
else:
raise ValueError("Unsupported file type or missing delimiter for text files.")
# Display the DataFrame before filtering
print("DataFrame before filtering:")
display(user_file.head())
# Get the initial count of rows in the DataFrame
start_count = len(user_file)
# Apply column filters
for column, filters in column_filters.items():
if column not in user_file.columns:
print(f"Warning: Column '{column}' does not exist in the DataFrame.")
continue
filter_condition = pd.Series([False] * len(user_file))
for filter_value in filters:
if pd.api.types.is_string_dtype(user_file[column]):
filter_condition |= user_file[column].str.contains(filter_value, case=False, na=False)
elif pd.api.types.is_numeric_dtype(user_file[column]):
try:
filter_value_numeric = float(filter_value)
filter_condition |= (user_file[column] == filter_value_numeric)
except ValueError:
print(f"Warning: '{filter_value}' is not a valid number for column '{column}'.")
else:
print(f"Warning: Column '{column}' has unsupported data type for filtering.")
user_file = user_file[filter_condition]
# Display the filtered DataFrame
print("Filtered DataFrame:")
display(user_file)
# Get the count of rows in the filtered DataFrame
count = len(user_file)
# Calculate the sum of specified columns in the filtered DataFrame
total_sums = {col: user_file[col].sum() for col in sum_columns} if sum_columns else None
# Output results
print(f"Total number of rows in the file before filtering: {start_count}")
print(f'Count of filtered entries: {count}')
if sum_columns:
for col, total in total_sums.items():
print(f'Total sum of {col} in filtered entries: {total}')Evaluate
The Evaluate plugin is designed to help developers evaluate code snippets. It is particularly useful for those who want to quickly see what improvements can be made to the code snippet.
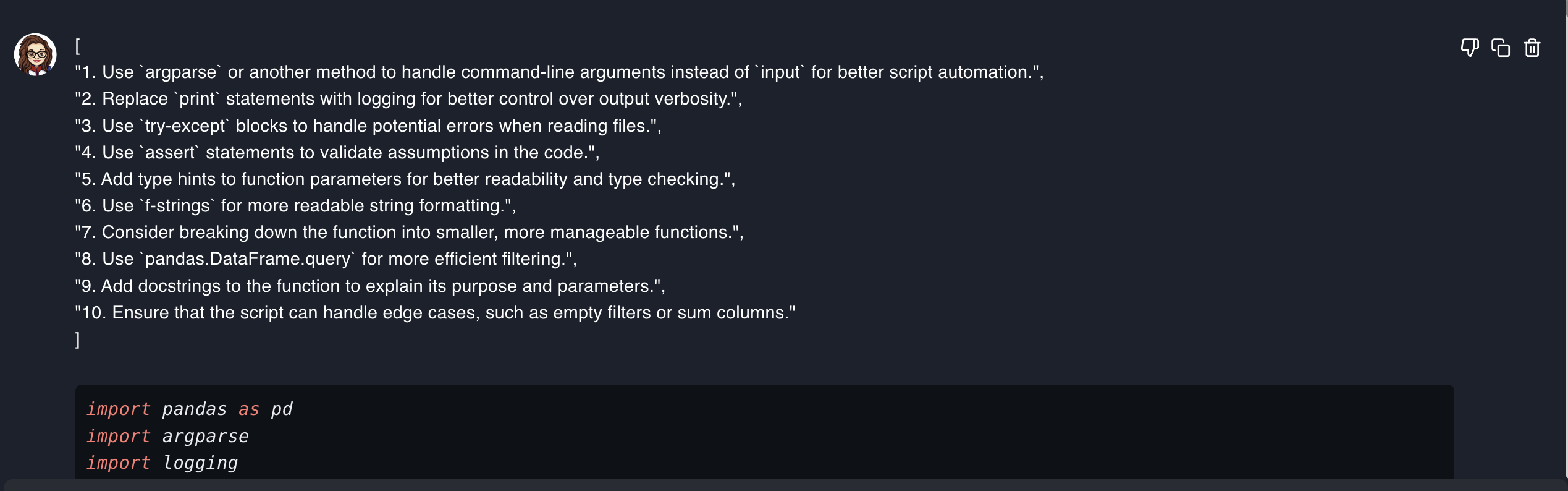
Ask Sage provides a detailed explanation of the improvements that can be made to the code snippet. This can help developers understand the best practices and coding standards that should be followed.
import pandas as pd
import argparse
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
def filter_and_sum_function(file_path: str, column_filters: dict, delimiter: str = None, sum_columns: list = None):
"""
Filters a DataFrame based on given column filters and calculates the sum of specified columns.
Parameters:
file_path (str): Path to the input file.
column_filters (dict): Dictionary where keys are column names and values are lists of filter values.
delimiter (str, optional): Delimiter for reading text files. Defaults to None.
sum_columns (list, optional): List of columns to sum. Defaults to None.
"""
try:
if file_path.endswith('.xlsx'):
user_file = pd.read_excel(file_path)
elif file_path.endswith('.txt') and delimiter:
user_file = pd.read_csv(file_path, delimiter=delimiter)
else:
raise ValueError("Unsupported file type or missing delimiter for text files.")
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"Error reading file: {e}")
return
logging.info("DataFrame before filtering:")
logging.info(user_file.head())
# ... rest of improved code with proper logging and error handlingKey Improvements Made:
Evaluate plugin to see further improvements that can be made to the code snippet after each iteration. This not only helps with code improvement but also increases the productivity of developers. Get Code from GitHub Page
The Get Code from GitHub Page plugin is designed to help developers extract code snippets from GitHub pages quickly. There are many instances where developers need to refer to code snippets from GitHub repositories, and this plugin makes it easy to do so.
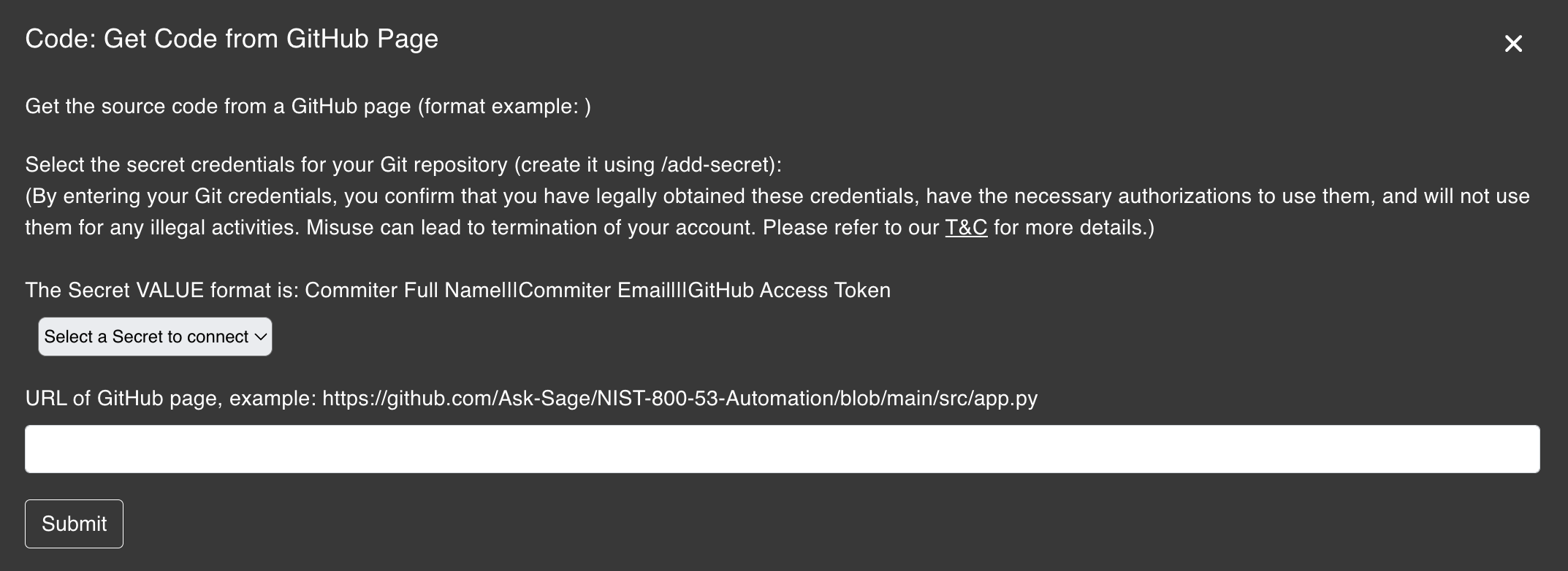
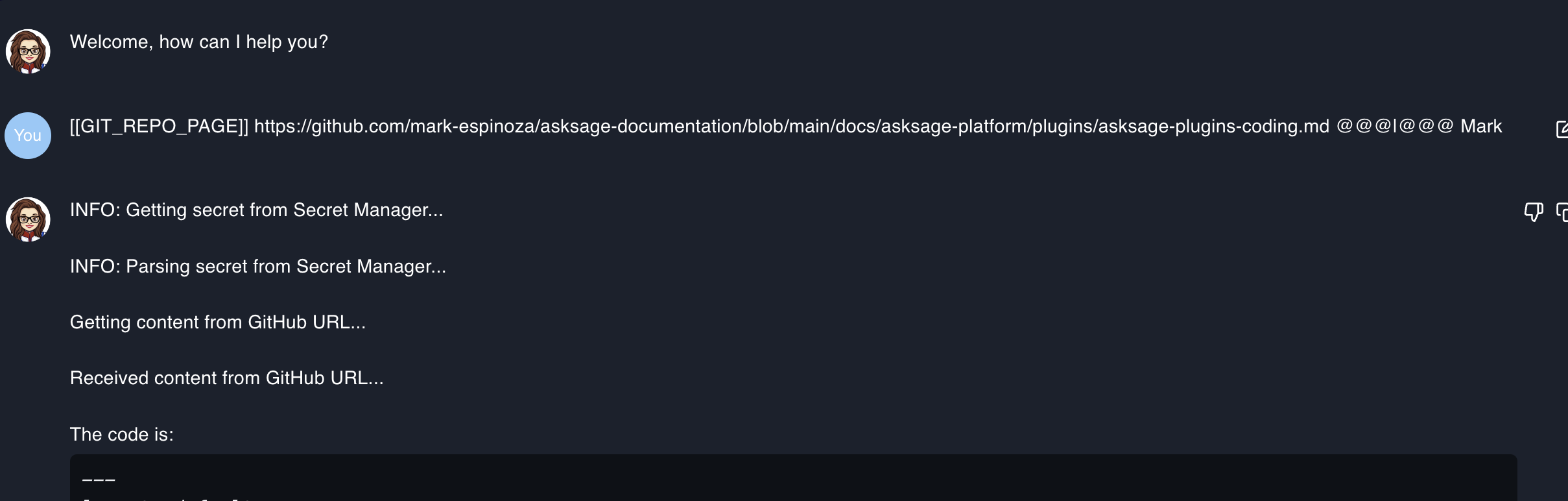
Git Repository Analysis
The Git Repository Analysis plugin scans a Git repository for security vulnerabilities, performance issues, and other problems. This plugin is useful for developers who want to ensure the quality and security of their codebase.
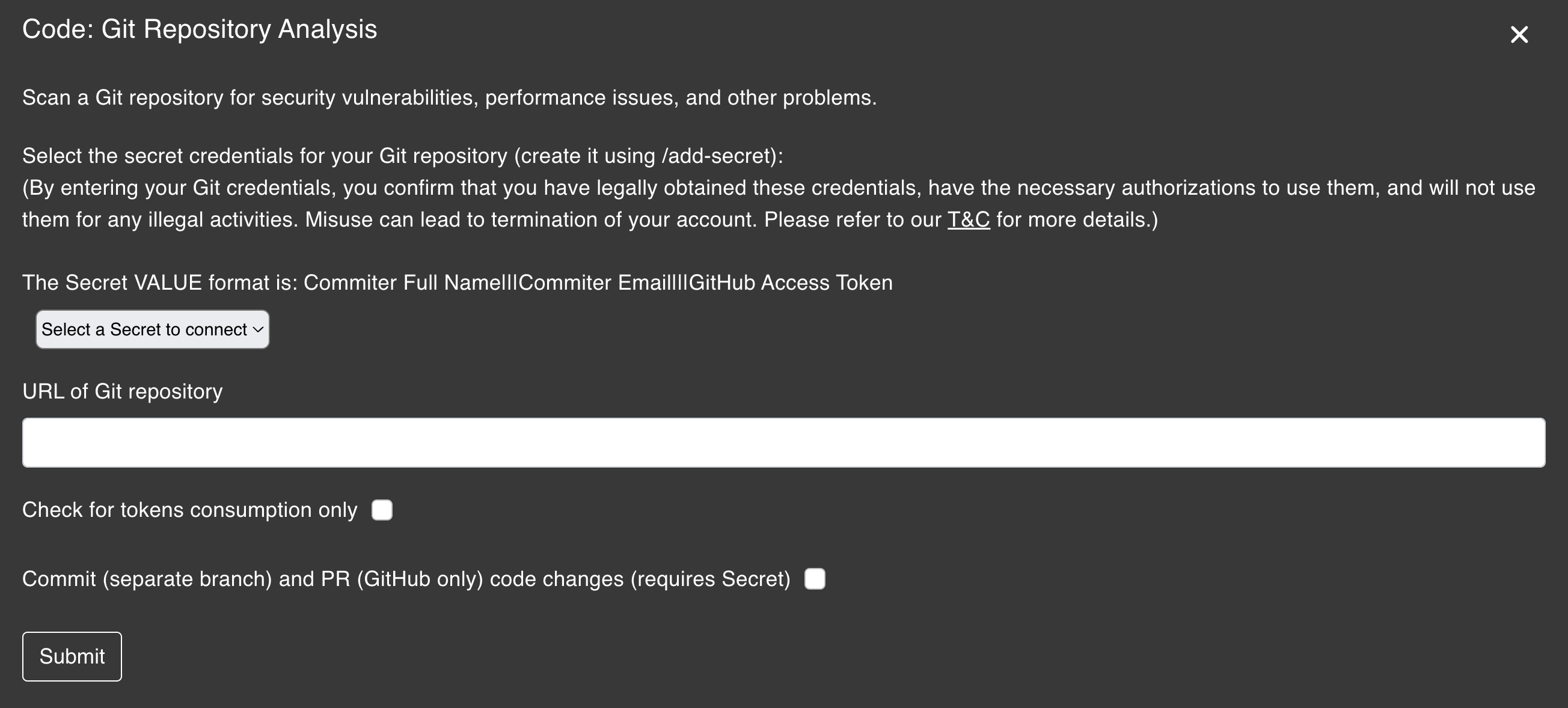
Get Code from GitHub Page plugin section above. Search GitHub Repository
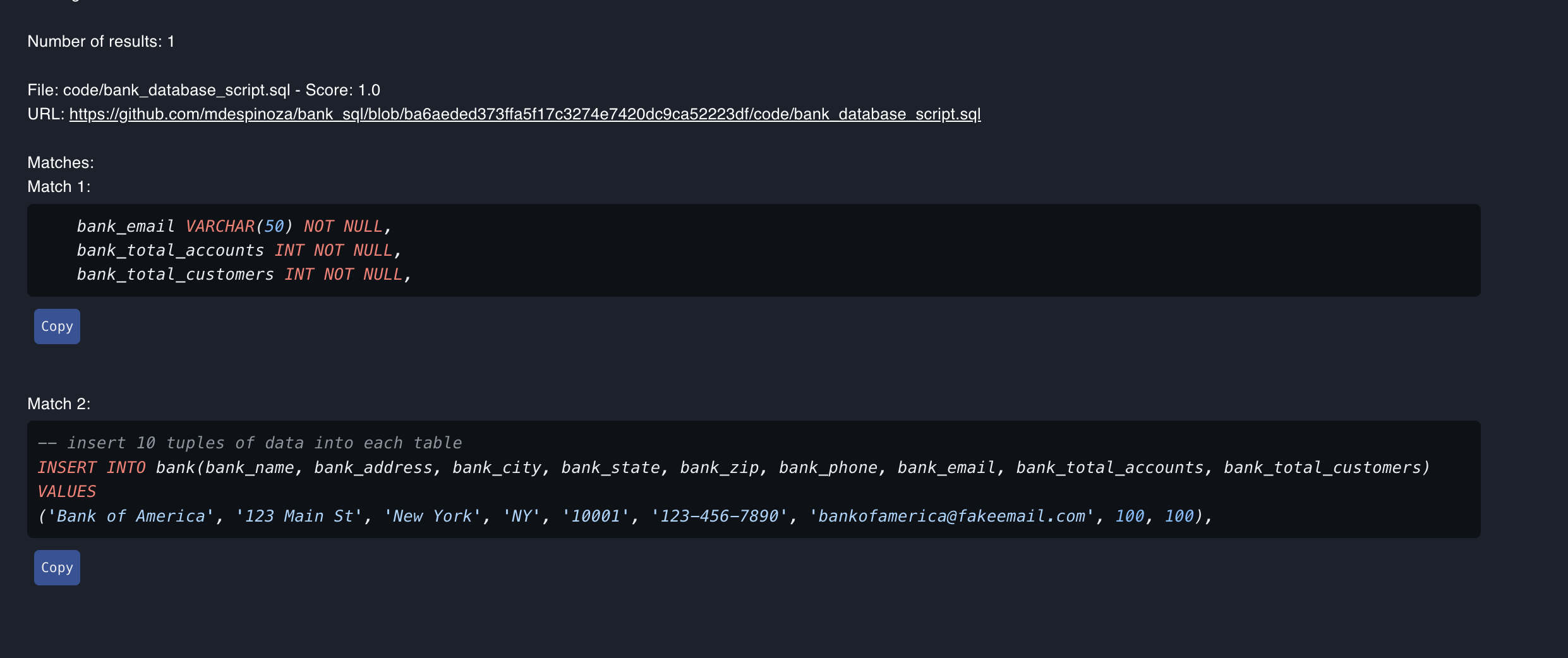
The Search GitHub Repository plugin is designed to help developers search a GitHub repository for specific code snippets. This plugin is useful for developers who want to quickly find code snippets in a large codebase or repository.
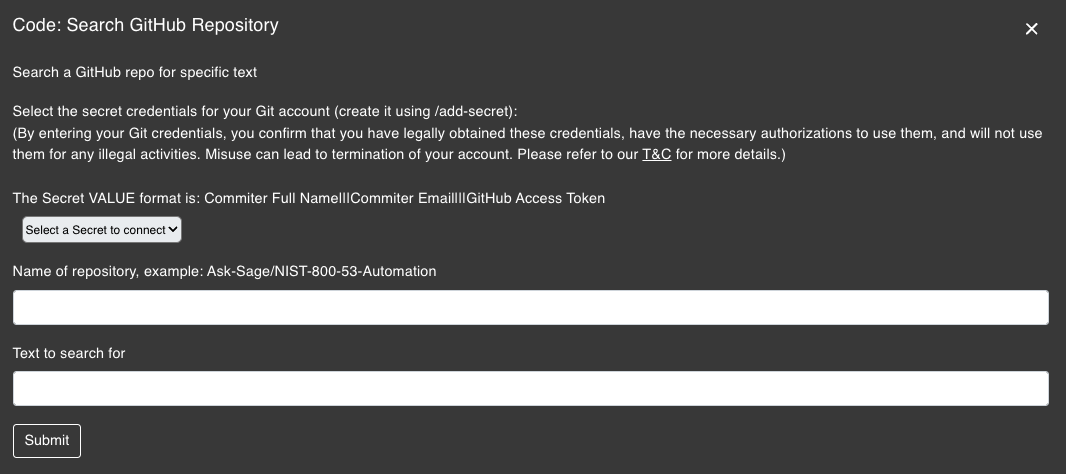
Searching for the field bank_total_accounts in a repository for a fictitious bank.
# Search term:
bank_total_accounts
# Results found in 3 files:
# File: src/models/account.py (Line 45)
class BankAccount:
bank_total_accounts = 0 # Class variable to track total accounts
# File: src/services/analytics.py (Line 128)
def get_statistics(self):
return {"total": bank_total_accounts}
# File: tests/test_accounts.py (Line 23)
assert bank_total_accounts == 100